Cast Iron Forging | Step by Step Guide
Updated: 17 Nov 2024
734
Introduction
When it comes to manufacturing strong, durable, and reliable components, cast iron forging plays a pivotal role. This process transforms raw cast iron into tough and precise parts by shaping it under immense pressure and controlled heat. Unlike casting, where molten metal is poured into molds, forging enhances the metals structural integrity by aligning its grain structure.
Cast iron forging is widely used in industries such as automotive, construction, and heavy machinery due to its superior strength and ability to withstand demanding conditions. From creating robust gears to long lasting valves, forged cast iron components have become indispensable in modern engineering.
This article will guide you through the fascinating world of cast iron forging, highlighting its processes, advantages, and applications. Whether you are a manufacturing enthusiast or simply curious about industrial techniques, you are in for an insightful journey.
What is Cast Iron Forging?
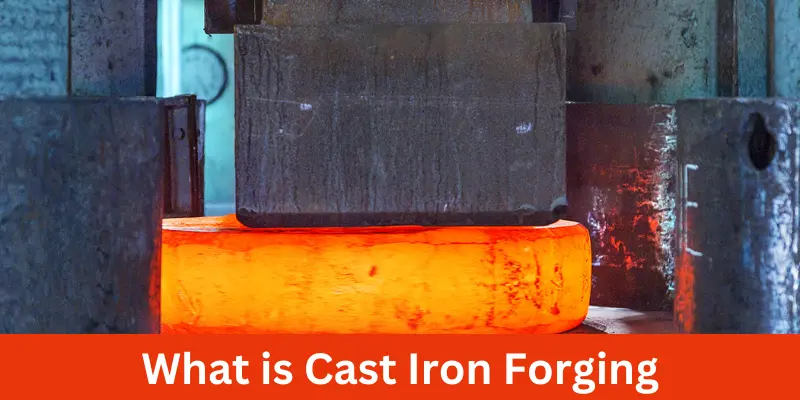
Imagine you have a piece of dough, and you press and shape it to make a cookie. Cast iron forging is a bit like that but with metal, Instead of dough, it uses cast iron, a strong and heavy type of metal. The metal is heated until its soft enough to shape, but not melted. Then, big machines or hammers press it into the shape we want.
This process makes the metal stronger and tougher, like how kneading dough makes it smoother and better for baking. Forged cast iron parts are used to make things like car parts, tools, and even big machines. They are strong, durable, and can handle heavy work without breaking.
You May Also Visit It!
Spray Arc Welding – Step by Step Guide – Need Metals
Pre Coat Metal | Define Complete Guide- Need Metals
Mcelroy Metals – Types, Uses And Properties – Need Metals
Will Magnets Stick to Stainless Steel Refrigerator – Complete Guide
The Forging Process
The forging process is like crafting something amazing out of metal, just like a sculptor shaping clay. Here how it works step by step:
1. Heating the Metal
- The first step is to heat the cast iron. Its placed in a super hot furnace to make it soft but not liquid, like how you warm clay to make it easier to shape.
2. Shaping the Metal
- Once the metal is soft, big machines or hammers press, hit, or squeeze it into the desired shape. Imagine using cookie cutters, but much stronger and more precise. This helps shape the metal while making it stronger.
3. Cooling Down
- After shaping, the metal is left to cool and harden. During this stage, it becomes super tough and ready for use.
4. Finishing Touches
- Just like decorating a cake, the forged metal might need some polishing or trimming to make it perfect for its job.
Forging makes the metal much stronger than other methods like casting, where the metal is poured into a mold. This is why forged parts are used in things like cars, machines, and tools they need to be really strong.
Cast Iron Forging vs. Other Processes
When making things from metal, there are different ways to shape it. Two popular methods are forging and casting, but they work in very different ways.
What is Forging?
Forging is like shaping clay with your hands, but with metal. The metal is heated until its soft but not melted. Then, large machines or hammers press and squeeze it into the desired shape. Forging makes the metal super strong because it aligns the tiny particles inside, like stacking bricks neatly to build a solid wall.
What is Casting?
Casting is more like pouring chocolate into a mold to make candies. The metal is heated until it melts into a liquid. This liquid metal is then poured into a mold of the desired shape. Once it cools and hardens, you get your metal part. Casting is great for making complex shapes that forging can not easily create.
How Are They Different?
1. Strength
- Forged parts are usually stronger and tougher because the metal is squeezed tightly together during forging. Cast parts can sometimes have tiny air bubbles inside, which makes them weaker.
2. Shape Complexity
- Casting can create very detailed and complicated shapes because the liquid metal fills every corner of the mold. Forging, on the other hand, is better for simpler, stronger shapes.
3. Uses
- Forged parts are used where strength is super important, like in cars, planes, or big machines. Cast parts are used when detailed shapes are needed, like in decorations or small machine parts.
Which is Better?
It depends on what you need. If you want something super strong and durable, like a car engine part, forging is the best choice. If you need something with lots of detail, like a fancy statue, casting is better.
Both processes are important and are used to make many things we use every day.
Applications of Cast Iron Forging
Cast iron forging is used in many important industries because of its strength and durability. Lets explore some places where forged cast iron parts are really helpful.
1. Automotive Industry
One of the most common uses for cast iron forging is in cars and trucks. Many important parts of a vehicle are made from forged cast iron because it is strong and can handle heavy use. For example, the engine parts (like pistons and crankshafts) are forged from cast iron to withstand high temperatures and pressure. These parts must be tough because they are used over and over again, especially in fast moving cars.
2. Machinery and Tools
Cast iron forged parts are also used in machines and tools that help make other products. Forged cast iron parts are found in things like industrial machinery, tools, and equipment that need to last for a long time and be able to handle a lot of stress. For example, gears, levers, and axles are often made from forged cast iron to make sure they do not break under pressure.
3. Construction and Heavy Equipment
In the construction industry, forged cast iron is used for parts in big machines, like excavators, cranes, and bulldozers. These machines need to be really strong because they lift heavy materials and work in tough conditions. Brackets, couplings, and frames are just a few examples of cast iron forged parts used in construction equipment. The strength of the forged metal makes these parts safe and reliable.
4. Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry also depends on cast iron forging for valves and pumps used in drilling and transporting oil. These parts need to handle high pressures and sometimes even extreme temperatures. Forged cast iron can withstand these tough conditions and last a long time without breaking.
5. Agriculture Equipment
Farmers use big machines like tractors and plows to help grow food. These machines are often made with forged cast iron parts because they have to work in difficult environments like fields with mud and rocks. Parts like tractor wheels or farm tool attachments are made strong with cast iron forging to make sure they last through the hard work they do.
6. Railways
Cast iron forging is also used in the railway industry. Train wheels, axles, and brakes are made from forged cast iron because they need to be strong and able to carry heavy loads across long distances.
As you can see, cast iron forging is used in many places where parts need to be strong, durable, and able to withstand tough conditions. Whether its in cars, construction equipment, or even farming tools, forged cast iron helps make sure these parts last a long time and can do their jobs well.
Future Trends in Cast Iron Forging

The world of cast iron forging is constantly evolving. As technology gets better, the ways we make and use forged cast iron parts are changing. Here are some exciting trends that might shape the future of cast iron forging:
1. Advanced Technology in Forging
- In the future, machines used for forging cast iron are going to get smarter and more precise. Robots and automated machines are already being used to make the process faster and more accurate. This means parts can be made more precisely and with less human effort. 3D printing is also being explored in metal forging, allowing for even more detailed and customized parts to be made.
2. Environmentally Friendly Forging
- As the world focuses on reducing pollution and conserving resources, the forging industry is also looking for ways to be greener. Recycling metal is becoming more important, and companies are finding ways to use less energy when forging cast iron. Some are even exploring ways to use cleaner energy sources like wind or solar power to help reduce the impact on the planet.
3. Lighter and Stronger Materials
- In the future, cast iron might be used in new ways thanks to advanced materials. Engineers are working on making cast iron lighter without losing its strength. This could lead to new uses in things like cars and airplanes, where parts need to be strong but not too heavy. Lighter materials would help vehicles use less fuel and travel faster.
4. Better Quality and Faster Production
- As technology improves, forging will become faster and more efficient. This will help companies make parts quicker and with higher quality, reducing costs and making it easier to produce products in larger numbers. This could make cast iron forging more affordable and available for more products in the future.
5. Customization and 3D Printing
- As 3D printing technology advances, we may see more customized forged cast iron parts. Instead of making many of the same parts, we could create unique ones designed specifically for a certain job or machine. This would be helpful in industries like aerospace or automotive where custom, strong parts are often needed.
These trends show that cast iron forging is not just about making strong parts its about making them better, faster, and more eco friendly. With new technologies, the future of forged cast iron is looking even more exciting.
You May Also Visit It!
Forging Process | Metal Becomes Tools and Parts – Easy Explanation
History of Nickel | From Ancient Coins to Modern Technology
Metal Does a Magnet Not Stick To | Uses and Types
Physical Properties Are Shared by Most Metals
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cast Iron Forging
Cast iron forging is widely used in industries due to its strength and durability. However, like any manufacturing process, it has both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Cast Iron Forging
| Advantages |
|---|
|
1. Strength and Durability
2. Improved Structural Integrity
3. Ability to Withstand High Temperatures
4. Customizable Shapes
5. Better Resistance to Wear and Tear
|
Disadvantages of Cast Iron Forging
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
1. High Cost of Equipment and Labor
2. Limited Design Flexibility
3. Energy Consumption
4. Risk of Material Waste
5. Size Limitations
|
Cast iron forging offers excellent strength, durability, and performance in demanding environments. However, its more expensive and may not be suitable for very intricate designs or very large parts. Like any manufacturing method, its essential to weigh the pros and cons based on the specific needs of the project.
Common FAQs About Cast Iron Forging
Here are some frequently asked questions about cast iron forging, answered in a simple and easy to understand way:
What is cast iron forging?
Cast iron forging is the process of shaping cast iron by applying heat and pressure to it. Unlike casting, where the iron is poured into molds, forging involves hammering or pressing the metal while it is hot to change its shape. This process makes the iron stronger and more durable.
Why is forged cast iron stronger than regular cast iron?
Forged cast iron is stronger because the forging process aligns the metals internal grain structure. When cast iron is forged, the metal is compressed, which reduces weaknesses like air pockets or cracks that might be present in cast iron that was simply poured into a mold. This makes forged cast iron parts much more reliable.
What are the main uses of cast iron forging?
Cast iron forging is used in many industries, including:
- Automotive: Parts like pistons and crankshafts in cars.
- Machinery: Industrial tools and equipment.
- Construction: Heavy duty equipment like bulldozers and cranes.
- Oil and Gas: Valves and pumps used in drilling.
- Agriculture: Farming machinery like tractors and plows.
Can cast iron be forged into any shape?
While cast iron can be forged into many shapes, there are some limitations. The forging process works best for parts with simpler or moderate shapes. For very complex or detailed shapes, casting might be a better option because molten metal can flow into more intricate molds.
Is cast iron forging expensive?
Yes, cast iron forging can be more expensive compared to other manufacturing methods. This is because it requires specialized equipment, skilled labor, and a lot of energy to heat and shape the metal. However, the long lasting durability and strength of forged cast iron parts can make it worth the cost in certain applications.
What are the advantages of cast iron forging over other processes?
Cast iron forging offers several advantages:
- Strength and durability: It creates stronger, more reliable parts.
- Better resistance to wear: Forged cast iron can handle heavy use and wear.
- Improved structural integrity: The grain structure of the metal becomes more uniform, reducing defects.
What are the disadvantages of cast iron forging?
Some disadvantages include:
- High costs: The process is more expensive because of the equipment and labor needed.
- Limited design flexibility: Forging works best for simpler parts; complex designs are better suited for casting.
- Energy consumption: Forging can use a lot of energy, which can increase costs and environmental impact.
Can cast iron forging be used for large parts?
Forging works best for medium sized parts. For very large parts, it can become impractical, as the machinery and process required to forge them are much bigger and more expensive. In such cases, other processes like casting or machining might be preferred.
These FAQs should give you a clearer understanding of what cast iron forging is, how it works, and its pros and cons.
Bonus Points on Cast Iron Forging
1. Versatility in Use
- Cast iron forging can be used in a wide variety of industries, from automotive to agriculture. Parts made from forged cast iron are commonly used in engines, heavy machinery, and construction equipment. This versatility makes it a crucial process in creating reliable, high performance components.
2. Better Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Forged cast iron performs exceptionally well in environments that require high strength and resistance to wear, such as in high pressure systems or machinery exposed to extreme temperatures. The forging process helps eliminate air pockets and weaknesses found in cast iron, resulting in parts that last longer and can withstand harsher conditions.
3. Long Term Cost Savings
- While the initial cost of forging cast iron parts is higher, they often provide long term cost savings. The increased durability and performance of forged parts lead to fewer breakdowns, reduced maintenance costs, and a longer lifespan compared to parts made through other methods like casting or machining.
4. Customization and Precision
- Cast iron forging allows for the creation of custom, high precision parts tailored to specific needs. This makes it ideal for industries that require unique components or parts with exact specifications, such as aerospace and defense.
5. Reducing Environmental Impact
- With the growing focus on sustainability, the forging industry is also exploring ways to reduce its environmental impact. Advances in recycling techniques, energy efficient machinery, and the use of renewable energy sources are making cast iron forging more eco friendly.
These bonus points highlight the importance of cast iron forging in manufacturing high quality, durable components across various sectors. As technology continues to evolve, the benefits of this process will likely expand even further.
Conclusion
Cast iron forging is a powerful manufacturing process that creates strong, durable parts used in many industries. By heating and shaping cast iron under pressure, it improves the metals strength, making it ideal for heavy duty applications like automotive and machinery parts.
While it has its challenges, like higher costs and energy use, the benefits of better performance, reliability, and wear resistance make it a preferred choice for critical components. As technology improves, cast iron forging is likely to become more efficient and environmentally friendly, offering even more possibilities for the future.
You May Also Visit It!
Magnetic Materials | What Materials Are Attracted By Magnets – Benefits
Yield Strength of Metals: Types, Uses and Clear and Simple Overview
Heat Treating Steel | Key Temperatures for Hardening, Types and Uses
1075 or 1095 Steel | Find the Best Steel for Your Knife
Aluminium Metal, Types, Uses, Properties and Rust Aluminium
Please Write Your Comments