What Is Piston | Step by Step Guide | Metals
Updated: 10 Dec 2024
610
A piston is a small but crucial component found in many machines, especially in engines. It is a cylindrical part that moves up and down inside a hollow chamber, often referred to as a cylinder. In internal combustion engines, the piston plays a vital role by transferring the force generated by fuel combustion into mechanical energy, powering your vehicle or machine. What Is Piston can also be found in other systems, such as hydraulic or pneumatic devices, where they help create or control pressure.
Although they might seem like simple parts, pistons are designed with precision and need to withstand extreme conditions, including high heat and pressure. Over the years, technology has advanced, and today is pistons are made from durable materials like aluminum or steel to improve their performance and longevity. Understanding how a piston works, the materials it is made of, and how to maintain it can give you a deeper appreciation for the engines and machines we rely on daily.
What Is Piston?
A piston is a key component in many engines, typically made of metal, and shaped like a cylindrical rod. Its main job is to move up and down inside a cylinder to convert energy, usually from fuel combustion, into mechanical force. This force is then used to power various machines, like cars, motorcycles, and even aircraft.
In internal combustion engines, the piston is driven by the explosion of fuel in the combustion chamber, which pushes the piston downward.

This motion turns the crankshaft, which ultimately powers the wheels or propels the machine forward. Pistons are crucial to this process, making them one of the most important parts of an engine.
The design of pistons can vary depending on the type of engine and the materials used. Pistons are typically made from durable materials like aluminum or steel, as these metals can withstand the high temperatures and pressures inside the engine. They are also equipped with piston rings that help seal the combustion chamber and prevent leaks, ensuring efficiency and performance.
You May Also Visit It
Copper Zinc Alloys – Step by Step Guide
Cast Iron Melting Temp | Discover Its Industrial Secrets
Is Aluminium Magnetic Material | Types, Uses and Properties
Physical Properties Are Shared by Most Metals
Types of Piston
There are different types of pistons, each designed for specific engines and machines. Lets take a look at some of the most common types:
1. Cast Pistons
- What are they? Cast pistons are made by pouring molten metal into a mold to create their shape. This is a simple and cost effective method.
- Where are they used? They are usually found in standard car engines and are great for regular use, as they are durable and affordable.
2. Forged Pistons
- What are they? Forged pistons are made by heating metal and then shaping it under intense pressure. This process makes them stronger than cast pistons.
- Where are they used? Forged pistons are used in high performance engines, such as race cars or sports vehicles, because they can handle more heat and stress.
3. Hypereutectic Pistons
- What are they? These pistons are made from a special alloy of aluminum with a higher silicon content. The extra silicon makes them harder and more resistant to wear.
- Where are they used? Hypereutectic pistons are often used in everyday cars and engines that need to run smoothly but do not need to be high performance.
4. Aluminum Pistons
- What are they? Aluminum pistons are lightweight and great at transferring heat, making them ideal for engines that get really hot.
- Where are they used? These are commonly used in most modern car engines because they help reduce engine weight and improve fuel efficiency.
5. Steel Pistons
- What are they? Steel pistons are made from a strong type of steel and are heavier than aluminum ones. They can withstand higher pressures and temperatures.
- Where are they used? These are often used in heavy duty machines like trucks and industrial engines, where power and durability are key.
Each type of piston has its own advantages depending on the engine is needs. Whether you are looking for something affordable, high performance, or durable, the right what is Piston type can make a big difference in how well an engine runs.
Making Process of Piston
Making a piston involves a careful and detailed process to ensure it is strong, durable, and works perfectly inside an engine. Here is how pistons are made:
1. Designing the Piston
First, engineers design the piston using computer software. They create a model of the piston, taking into account the size, shape, and material. This design is crucial because it must fit perfectly inside an engine is cylinder.
2. Choosing the Material
Pistons are typically made from metals like aluminum, steel, or a mix of both. Aluminum is lightweight and great at handling heat, while steel is stronger and more durable. The choice of material depends on the type of engine the piston is made for.
3. Casting or Forging
- Casting: In this step, molten metal is poured into a mold to form the piston. This method is cheaper but still makes strong pistons that work well in regular cars.
- Forging: Forging involves heating the metal until it is soft and then hammering it or pressing it into shape. This makes the piston stronger than a cast piston, and it is often used for high performance engines.
4. Machining the Piston
Once the piston is shaped, it is time to make it smooth and precise. Machines are used to shave off extra metal and make the piston the exact size and shape needed. This is where things like the piston rings and pin holes are added.
5. Adding Piston Rings
Piston rings are added to the piston to help seal the engine is combustion chamber, keeping the pressure in and preventing leaks. These rings also help the piston slide smoothly within the cylinder.
6. Finishing Touches
Finally, the piston is polished and coated to reduce friction. Sometimes, the piston is treated with special coatings that help it withstand high temperatures and last longer.
This process makes sure the piston is ready to handle the tough conditions it faces inside an engine, including high heat, pressure, and movement. It is a combination of careful design, high quality materials, and precise machining that makes pistons such an essential part of engine performance.
History of Piston
The history of the piston goes back a long way, all the way to the early days of machines and engines. Lets take a quick journey through time to understand how pistons became so important.
1. Early Beginnings
The piston is story begins in ancient times. The first known use of pistons dates back to the 1st century BC. The Greek inventor Heron of Alexandria created a steam powered device called the “aeolipile,” which is considered one of the first engines. While this early machine did not use a piston in the way we know it today, it was an important first step in understanding how steam could create motion.
2. Industrial Revolution
The real development of pistons as we know them started in the 18th century during the Industrial Revolution. Machines were becoming more powerful, and people were inventing engines that used pistons to generate force. One of the most famous inventors, James Watt, improved the steam engine in the late 1700s. Watt is engine used pistons to convert steam pressure into mechanical power, helping to drive machines and trains.
3. The Internal Combustion Engine
Fast forward to the late 19th century, and the invention of the internal combustion engine completely changed the role of pistons. This new type of engine used the explosion of fuel to push pistons up and down inside cylinders, turning this movement into mechanical energy. This was the type of engine used in early cars and airplanes. Karl Benz is credited with inventing the first true automobile in 1885, which used a piston engine.
4. Modern Pistons
Today, pistons are used in almost every kind of engine, from cars and trucks to airplanes and motorcycles. They have evolved to be much stronger and more efficient, made from materials like aluminum and steel. Engineers constantly improve piston design to make engines more powerful, efficient, and longer lasting.
From ancient steam powered devices to modern high tech engines, pistons have played a huge role in powering machines throughout history.
Elements of Piston
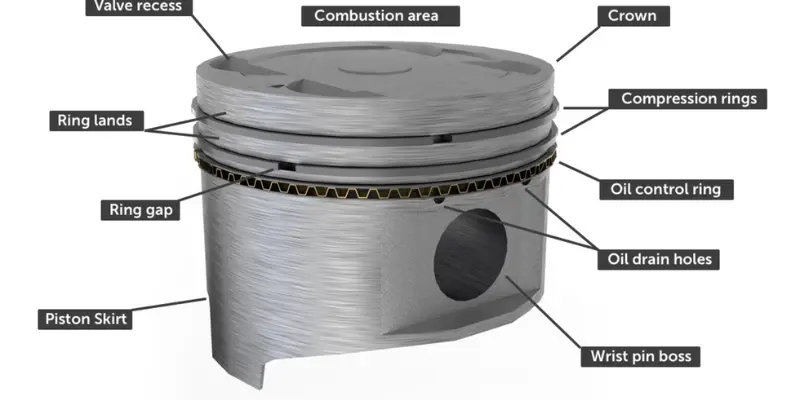
A piston is made up of several important parts that help it do its job inside an engine. Lets take a look at the main elements of a piston:
1. Piston Head (Crown)
- What is it? The piston head is the top part of the piston. It faces the combustion chamber where the fuel burns. This is where the explosion pushes the piston down.
- Why is it important? The piston head must be strong enough to withstand the pressure from the fuel explosion, and it often has a special shape to help the combustion process be more efficient.
2. Piston Skirt
- What is it? The skirt is the lower part of the piston that helps it stay centered in the cylinder.
- Why is it important? The skirt reduces the friction between the piston and the cylinder walls, helping the piston move smoothly without causing wear or damage.
3. Piston Rings
- What are they? Piston rings are circular metal bands that fit into grooves around the piston. There are typically two or three rings.
- Why are they important? These rings help seal the combustion chamber, keeping the pressure in while the fuel burns. They also help prevent oil from leaking into the combustion chamber and keep the piston moving smoothly.
4. Piston Pin (Wrist Pin)
- What is it? The piston pin is a small, cylindrical part that connects the piston to the connecting rod.
- Why is it important? The piston pin allows the piston to move up and down while transferring the energy from the piston to the rest of the engine.
5. Cooling Channels
- What are they? Some pistons have small passages or channels inside them for cooling fluid to flow through.
- Why are they important? These channels help keep the piston from getting too hot. Since pistons can get extremely hot from the combustion process, cooling them helps prevent damage and wear.
Each of these parts works together to help the piston do its job: converting the energy from burning fuel into movement that powers the engine. The design and materials used for each part are carefully chosen to ensure the piston performs efficiently and lasts a long time.
Properties of Piston
The piston has several important properties that help it perform its job inside an engine. Here are some of the key properties:
1. Strength
Pistons need to be very strong because they face a lot of pressure and heat during the engine is operation. The combustion process (where the fuel burns) creates powerful explosions that push the piston up and down. To handle these forces without breaking, pistons are made from strong metals like aluminum, steel, or a mix of both.
2. Durability
Since pistons are constantly moving up and down inside the engine, they must be able to last a long time. Pistons are designed to resist wear and tear. To make them last longer, they are often treated with special coatings or designed with heat resistant materials.
3. Lightweight
While pistons need to be strong, they also need to be light. If they were too heavy, the engine would struggle to move them quickly, reducing its efficiency. Lightweight materials like aluminum are often used to help reduce weight and improve engine performance.
4. Heat Resistance
Pistons get extremely hot during engine operation. Because of this, they need to be able to handle high temperatures without melting or warping. The material used for pistons, such as aluminum or steel, is chosen for its ability to resist heat. Some pistons even have cooling channels inside to help them stay cool.
5. Smooth Movement
Pistons must move up and down smoothly inside the cylinder. To help with this, they are often coated with materials that reduce friction. Friction can cause wear and reduce engine efficiency, so having a smooth moving piston is important for the engine is performance.
6. Sealing Ability
Pistons have piston rings that create a seal between the piston and the cylinder. This helps keep the combustion chamber tightly closed so that no gas escapes. The better the seal, the more efficient the engine is because it can use the fuel is energy without losing power.
These properties make pistons essential parts of an engine, ensuring that it works smoothly, efficiently, and for a long time.
You May Also Visit It
What is Ferrous vs Non Ferrous Metals – Complete Guide
What is Titanium Steel – Types, Uses, Properties and Modern Metal
Plasma Cutter How Does It Work – Complete Guide
Is Copper a Metalloid | Understanding the Classification of Elements
Advantages and Disadvantages of Piston
A piston is an important part of machines like cars and engines. In this post, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of pistons in simple terms.
| Pros |
|---|
|
| Cons |
|---|
|
Despite these disadvantages, pistons remain a crucial component in many machines, offering a balance of performance and affordability. Their continuous evolution ensures that they adapt to meet the demands of modern technology.
Common FAQs about Pistons
Pistons are an important part of engines, helping cars and machines run smoothly. In this article, well answer some common questions to help you understand pistons better.
What is a piston?
A piston is a cylindrical part inside an engine that moves up and down within a cylinder. It helps convert the energy from burning fuel into mechanical energy, which powers the engine. The piston plays a crucial role in internal combustion engines, like those in cars, motorcycles, and airplanes.
How does a piston work?
The piston works by moving up and down in a cylinder. When fuel burns in the combustion chamber, it creates a small explosion. This pushes the piston down, and the movement of the piston is what creates power. The piston is connected to a crankshaft, which turns this movement into rotational energy to power the vehicle or machine.
What are piston rings?
Piston rings are small metal bands that fit into grooves around the piston. They help seal the space between the piston and the cylinder, ensuring that no gases escape during combustion. Piston rings also help prevent oil from getting into the combustion chamber and help reduce friction between the piston and cylinder walls.
What materials are pistons made from?
Pistons are usually made from strong, lightweight materials like aluminum alloys or steel. Aluminum is often used because it is light and can withstand high temperatures. For high performance engines, pistons may be made with special coatings or treatments to make them even stronger and more heat resistant.
How long do pistons last?
Pistons can last for many years if properly maintained. However, over time, they may wear down due to the constant movement, heat, and pressure inside the engine. Regular maintenance, such as oil changes and using the engine within its recommended limits, can help extend the life of the pistons.
Can pistons be repaired or replaced?
Yes, pistons can be replaced if they become damaged or worn out. If a piston is severely damaged, it can affect the engine is performance, and replacement is necessary. Repairing a piston is usually not practical; instead, it is more cost effective to replace the piston and any damaged parts.
What happens if a piston breaks?
If a piston breaks or gets damaged, it can cause serious problems for the engine. The piston may seize, preventing the engine from running. It can also cause damage to other parts, like the cylinder walls or the crankshaft. It is important to fix a broken piston as soon as possible to avoid further engine damage.
Why is the piston important in an engine?
The piston is vital because it helps convert the energy from burning fuel into useful power. Without pistons, engines would not be able to function, as they are responsible for the movement that drives the vehicle or machinery. They are central to the engine is power producing process.
What are the types of pistons?
There are several types of pistons, including:
- Solid pistons: Simple, solid parts used in many engines.
- Forged pistons: Made from a stronger metal that is shaped under high pressure, commonly used in high performance engines.
- Cast pistons: Made by pouring molten metal into a mold, which is often cheaper and used in everyday vehicles.
How can I tell if my pistons need replacing?
Signs that pistons might need replacing include:
- Poor engine performance: If the engine loses power, it could be due to damaged pistons.
- Knocking sounds: If you hear unusual noises from the engine, it could mean the pistons are worn.
- Excessive smoke: Blue or gray smoke from the exhaust could indicate that oil is leaking into the combustion chamber, often caused by worn piston rings or pistons.
Conclusion
The piston is a vital part of an engine that helps turn fuel energy into mechanical power. It is designed to withstand extreme conditions, including heat, pressure, and friction. Pistons are made from durable materials like aluminum and steel to ensure long lasting performance.
While they are strong and efficient, regular maintenance is important to avoid wear and tear. Whether in cars, motorcycles, or other machines, pistons are essential for keeping engines running smoothly. By understanding how pistons work and taking care of them, we can ensure that our engines continue to perform well for years to come.
You May Also Visit It
Cast Iron Melting Temp | Discover Its Industrial Secrets
Metal Stamping Aluminum | Easy Steps to Understand Metal Stamping
Diagram of V8 Engine Explore the Power Behind Every Part
Welding Position | Types, Properties and Uses – Pros and Cons
What is Cold Roll Steel: Types, Grades and Uses | Pros and Cons
Please Write Your Comments