Types of Electrical Wire Explained – Need Metals
Updated: 29 Nov 2024
1061
Types of electrical wires are like the roads that electricity travels on to get to our homes and power things like lights, TVs, and computers. Without wires, we would not be able to use most of the electronics in our everyday life. There are many types of electrical wires, and each type is used for different jobs. In this article, we’ll learn about the different kinds of electrical wires, what they do, and why they are important.
Why Do We Use Electrical Wire?
Electrical wires are very important because they help us use electricity safely. Imagine electricity like water flowing through pipes. Wires are like the pipes that carry electricity to different places, like your house, school, or even your TV.
- Powering Things in Our Home: When you turn on a light, use your computer, or watch TV, the electrical wires are carrying the electricity to make those things work. Without wires, we wouldn’t be able to use many of the things we enjoy every day.
- Keeping Things Safe: Wires are also designed to keep us safe. They have special covers that make sure the electricity stays inside the wire and does not shock us. That’s why it’s important to never touch a wire when it’s plugged in.
You May Also Visit It
Copper Zinc Alloys – Step by Step Guide
Cast Iron Melting Temp | Discover Its Industrial Secrets
Is Aluminium Magnetic Material | Types, Uses and Properties
Physical Properties Are Shared by Most Metals
Types of Electrical Wire
Electrical wires come in different types, and each one is used for specific jobs. Let’s look at some of the most common ones:
Lets explain two types of Armored/ Metal Clad Wire:
- Non-Metallic (NM) Cable
- Underground Feeder (UF) Cable
- THHN/THWN Wire
- Armored Cable (AC) and Metal-Clad (MC) Cable
- Low-Voltage Wire
- Phone and Data Wire
- Coaxial Cable
- Speaker Wire?
- Ribbon Cable?
Non-Metallic (NM) Cable
This is one of the most common types of wires used in homes. It’s safe to use inside walls and is covered with a plastic coating to protect it from damage. People use it for things like lights, fans, and outlets.
Lets explain two types of building electrical wires:
- NM-B (“Romex”) Building Wire
- NM-B PCS Building Wire.
1. NM-B (“Romex”) Building Wire:
- What It Is: This is a common type of electrical wire used inside homes to carry electricity to outlets, lights, and appliances.
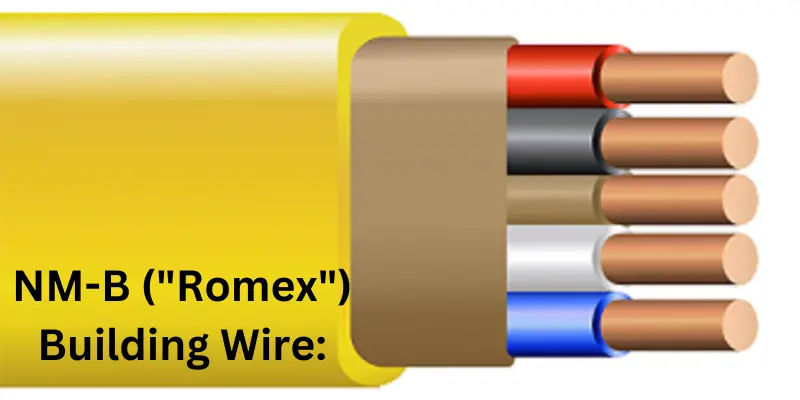
- Structure:
- It has a plastic outer cover that protects the wires inside.
- Inside, there are usually two or three smaller wires:
- Black or Red Wire: Carries electricity from the power source.
- White Wire: Returns electricity back, completing the circuit.
- Bare or Green Wire: Provides safety by grounding the circuit.
- Where It’s Used: Since it’s not designed to withstand moisture, it’s typically used in dry areas like bedrooms, living rooms, and hallways.
2. NM-B PCS Building Wire:
- What It Is: This wire is similar to the regular NM-B wire but includes extra wires for controlling things like dimmable lights.
- Structure:
- It has the same plastic outer cover.
- Inside, along with the usual wires, there’s an additional pair of smaller wires for sending control signals.
- Where It’s Used: It’s used in places where you need to control lighting levels, like in rooms with dimmer switches or smart lighting systems.
Parts of NM Cable
- Conductors: These are the metal wires inside that carry electricity.
- Insulation: This is the plastic around the wires that keeps them safe from touching other objects.
- Sheath: The outer layer of plastic that holds everything together.
Advantages of NM Cable
| Advantages |
|---|
|
Important Safety Tips
- Always turn off the power before working with electrical wires.
- Make sure the cable is not exposed to water as this can cause problems.
- Check if the wire is properly insulated to avoid dangerous accidents.
Underground Feeder (UF) Cable
This type of wire is special because it can be used outside and even buried underground. It’s strong and safe for outdoor electrical connections, like powering a garden light or an outdoor water pump.
Lets explain:
USE-2 Cable
- Standing for Underground Service Entrance, this cable is often used to bring power from utility lines to a building and is suitable for direct burial.
Installation Considerations:
- Depth Requirements: The National Electrical Code (NEC) specifies burial depths to ensure safety. For instance, UF cables typically need to be buried at least 24 inches deep.
- Protection Above Ground: Where the wire emerges from the ground, it should be protected with conduit to prevent physical damage.
Safety Tips:
- Use Appropriate Wire Types: Only use cables labeled for direct burial to ensure they can withstand underground conditions.
- Consult Local Codes: Always check local regulations and codes, as they may have specific requirements for burial depths and materials.
- Professional Installation: For complex installations, especially those involving high voltage, it’s advisable to consult a licensed electrician.
THHN/THWN Wire
This wire is used in a lot of places like buildings and factories. It’s covered with plastic and can handle high temperatures, which makes it perfect for places where there’s a lot of heat, like in factories or big electrical systems.
Lets explain five types of Electrical Wiring:
- THHN / MTW / THWN-2 / T90 Wire
- TFFN / TFN / TEWN Copper Building Wire
- TW-#8 Solid Green
- XHHW-2 / RW90
- USE-2 / RHH / RHW-2
1. THHN / MTW / THWN-2 / T90 Wire
- THHN: Imagine a sturdy garden hose that can handle hot water. THHN wire is like that hose, designed to carry electricity safely in dry places. It’s commonly used in homes and buildings.
- MTW: Think of a flexible straw that can bend easily. MTW wire is similar because it’s very flexible and is used inside machines where wires need to move around.
- THWN-2: Picture a raincoat that keeps you dry. THWN-2 wire has a special jacket that allows it to work safely in wet places, like outdoors or in basements.
- T90: This is just another name for THHN wire used in Canada. It’s like calling a soccer game “football” in other countries they mean the same thing.
2. TFFN / TFN / TEWN Copper Building Wire
- TFFN: Imagine a thin, flexible shoelace. TFFN wire is thin and flexible, making it perfect for connecting light fixtures and small appliances.
- TFN: Similar to TFFN but less flexible, like a stiff shoelace. It’s used where flexibility isn’t as important.
- TEWN: This wire is designed to resist moisture and chemicals, like a kitchen glove. It’s used in places where it might get wet or oily.
3. TW-#8 Solid Green
- TW: Think of a simple rubber-coated wire. TW wire has a rubbery coating and is used for general wiring in homes.
- 8 Solid Green: The “#8” tells us it’s a specific thickness, like a thick piece of spaghetti. The green color means it’s used for grounding, which is like providing a safe path for electricity to go into the ground if there’s a problem.
4. XHHW-2 / RW90
- XHHW-2: Imagine a heavy-duty extension cord that can handle high heat and moisture. XHHW-2 wire is tough and used in places like factories where conditions can be harsh.
- RW90: This is the Canadian name for a similar wire. It’s like how some people call soda “pop” different names for the same thing.
5. USE-2 / RHH / RHW-2
- USE-2: Picture a waterproof cable that can be buried underground, like a garden hose buried to water plants. USE-2 wire is used to bring electricity to buildings from an underground source.
- RHH: This wire is like a heat-resistant glove, designed to handle high temperatures. It’s used inside buildings where it might get hot.
- RHW-2: Similar to RHH but also resistant to water, like a waterproof oven mitt. It’s used in places that are both hot and wet.
By comparing these wires to everyday items, it’s easier to understand their unique features and where they are used.
Key Differences:
- Extra Control Wires: NM-B PCS has additional wires for controlling devices, while regular NM-B does not.
- Usage: NM-B PCS is used for advanced lighting controls, whereas NM-B is for standard electrical needs.
Both types of wires are like special roads that carry electricity to different parts of your home. The NM-B wire is for regular electrical needs, while the NM-B PCS wire has extra features for controlling things like dimmable lights.
Armored Cable (AC) and Metal-Clad (MC) Cable
These wires have a strong metal covering that helps protect them from being damaged. This is a good choice for areas where the wire could get hit or broken, like in garages or basements.
Lets explain two types of Armored/ Metal Clad Wire:
- MC Steel Armor (MC-SL) Cable
- MC Aluminum Armor (MC-AL) Cable
- MC Fire Alarm & Control Cable
- MC-LED Cable
- AC HCF Aluminum/Steel Armor (HCF-AL) Cable
- MC-LED Healthcare Cable
- PVC Jacketed MC Cable
- MC Steel Armor (MC-SL) Cable
- This cable has a strong steel jacket, like a knight’s armor, protecting the wires inside.
- It’s used in places where the cable might get bumped or scratched, keeping the electricity flowing safely.
- MC Aluminum Armor (MC-AL) Cable
- MC Fire Alarm & Control Cable
- This special cable connects fire alarms and control systems.
- It’s designed to work even in high heat, ensuring alarms can alert us during a fire.
- MC-LED Cable
- Made specifically for LED lighting systems, which are energy-efficient lights.
- Helps in reducing energy use and keeps lighting systems organized.
- AC HCF Aluminum/Steel Armor (HCF-AL) Cable
- “HCF” stands for Health Care Facilities.
- These cables are used in hospitals and have extra protection to ensure medical equipment works reliably.
- MC-LED Healthcare Cable
- Combines features of MC-LED and HCF cables.
- Used in healthcare settings to power LED lights, ensuring both energy efficiency and safety.
- PVC Jacketed MC Cable
- This cable has a plastic jacket (PVC) that protects it from moisture and sunlight.
- It’s used outdoors or in wet places to keep the electricity flowing safely.
Choosing the Right Cable
- Just like choosing the right tool for a job, it’s important to pick the correct cable for each use.
- Using the right cable ensures safety and that everything works properly.
You May Also Visit It
What is Ferrous vs Non Ferrous Metals – Complete Guide
What is Titanium Steel – Types, Uses, Properties and Modern Metal
Plasma Cutter How Does It Work – Complete Guide
Is Copper a Metalloid | Understanding the Classification of Elements
Low-Voltage Wire
These wires carry a smaller amount of electricity and are used for things that do not need a lot of power, like doorbells, security systems, or landscape lights.
Lets explain two types of low voltage wire:
- Two Wire System
- Three Wire System
1. Two Wire System
- What It Is: This system uses two wires to carry electricity to devices.
- Components:
- Live Wire (Hot Wire): Carries electricity from the power source to the device.
- Neutral Wire: Completes the circuit by carrying electricity back to the power source.
- Common Uses: Found in older homes and simple devices like lamps and small appliances.
- Safety Note: Many two-wire systems lack a ground wire, which can be unsafe. It’s important to ensure devices are properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks.
2. Three-Wire System
- What It Is: This system uses three wires to provide electricity.
- Components:
- Two Live Wires (Hot Wires): Carry electricity to the device.
- Neutral Wire: Carries electricity back to the power source.
- Ground Wire: Provides a safe path for electricity to flow into the ground in case of a fault.
- Common Uses: Used in modern homes and for devices that need more power, like air conditioners and electric stoves.
- Safety Note: The ground wire adds an extra layer of safety by directing stray electricity safely into the ground.
Phone and Data Wire
These wires are used to carry signals for things like phones, internet, and TV. They are not used for power but for connecting devices to each other.

Lets explain three types of phone and data wire:
- Coaxial Cable:
- Twisted Pair Cable:
- Fiber Optic Cable:
1. Coaxial Cable
- Used for connecting TVs and internet modems.
- Has a metal core for sending signals, wrapped in insulation to protect it.
2. Twisted Pair Cable:
- Contains pairs of wires twisted together.
- Used for telephone lines and internet connections.
3. Fiber Optic Cable:
- Transmits data using light signals instead of electricity.
- Can carry a lot of information over long distances without losing quality.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable is a special kind of wire used to carry information like TV signals, internet, and phone calls. It looks like a long tube with multiple layers inside to protect the information it carries.
Coaxial cables have three main parts:
- Inner conductor: This is the center part of the cable. It’s made of metal (usually copper) and carries the electrical signals.
- Insulation: This is the layer around the inner conductor that keeps it safe and prevents the signals from getting lost.
- Outer conductor: This part is made of metal mesh or a foil layer. It helps protect the signals from getting mixed up with other signals and also shields the cable from outside interference.
- Outer jacket: The final layer is a plastic cover that protects everything inside the cable from getting damaged.
How Does Coaxial Cable Work?
Coaxial cable carries information in the form of electrical signals. These signals travel through the inner conductor and are protected by the other layers. This helps the signals stay strong and clear without getting interfered with by other things around them, like radio waves or electrical noise.
Uses of Coaxial Cable
- TV: Coaxial cables are commonly used to bring cable TV signals to your home.
- Internet: Many internet companies use coaxial cables to connect your home to the internet.
- Phones: Some phone systems use coaxial cables to send signals.
Speaker Wire?
Speaker wire is a special type of wire used to connect speakers to your sound system, like a stereo or a home theater. It carries the sound signal from your system to the speakers so you can hear music or sound effects.
Speaker Wire Used
- Connecting speakers to audio systems: When you hook up a speaker to a sound system (like a TV, stereo, or computer), you use speaker wire to make the connection.
- Home theaters: Speaker wire helps deliver sound in a home theater system so you can enjoy movies with great audio.
- Car audio systems: It’s also used in cars to connect the speakers to the car’s sound system.
Types of Speaker Wire
- Two-Conductor Wire: This is the most common type. It has two wires inside – one for positive (+) and one for negative (-) connections.
- Multi-Conductor Wire: This type has more than two wires, and it’s used for connecting more than one speaker or for complex setups.
- Thin and Thick Wires: Speaker wire comes in different thicknesses. Thicker wire is used for bigger speakers that need more power.
Safety Tips
- Make sure to turn off the power when connecting the wire to avoid any electric shocks.
- Never cut or damage the speaker wire, because it can stop the sound from coming out.
- If you’re unsure, ask an adult to help you connect the speaker wire properly.
Ribbon Cable?
Ribbon cable is a special type of wire that looks like a flat, wide strip. It’s made of many smaller wires that are placed side by side, just like a ribbon. The wires inside are usually very thin and run parallel to each other.
Ribbon Cable Used
- Connecting Computers: Ribbon cables are often used inside computers to connect different parts like the hard drive and the motherboard.
- TVs and Other Electronics: They help connect parts inside TVs, printers, and other electronic devices.
- Organizing Wires: Because the wires are flat and neatly lined up, ribbon cables help keep things organized and easy to manage.
What Makes Ribbon Cables Special?
- Flat Design: Ribbon cables are flat, so they are easy to fold and fit in small spaces.
- Space-Saving: They can be used in tight places where regular round cables wouldn’t fit.
- Flexibility: Even though it’s flat, the ribbon cable is flexible, making it easy to move around without breaking.
Safety Tips When Using Ribbon Cable
- Be Careful with the Wires: Do not bend the ribbon cable too much because the wires inside can break.
- Keep It Clean: Dust and dirt can make the cable stop working, so keep it clean and dry.
Choosing the Right Electrical Wire
When you are picking an electrical wire, there are some important things to think about to make sure it’s safe and works the best for what you need. Here’s how you can choose the right wire:
Think About the Voltage
- The voltage tells you how strong the electricity is. Make sure the wire can handle the right amount of voltage for the job.
Consider the Current
- The current is the flow of electricity. Pick a wire that can carry the right amount of current without overheating.
Check the Environment
- Is the wire going to be used inside or outside? Some wires work better in wet places, and others are better for dry, indoor spaces. Think about where you’ll use the wire.
Pick the Right Insulation
- The insulation is the covering around the wire. It protects the wire and helps keep electricity from escaping. Some wires have stronger insulation for more safety.
Look for Safety Marks
- Always look for safety labels on wires. These show that the wire meets safety rules and is good quality.
- Ask for Help if You’re Unsure
If you are not sure which wire to choose, ask an expert like an electrician. They can help you make the best choice for your project.
Safety Tips to Uses Electrical Wire
When working with electrical wires, it’s very important to stay safe! Here are some simple safety tips to follow:
- Always Turn Off the Power: Before you do anything with electrical wires, make sure to turn off the power. This keeps you from getting shocked.
- Wear Protective Gear: Use rubber gloves and safety glasses. They protect you from getting hurt if something goes wrong.
- Check the Wire’s Rating: Always check if the wire can handle the amount of electricity you need. Using the wrong wire can be dangerous.
- Avoid Water: Never work with electrical wires if there’s water around, like in a wet basement or outside during rain, because water can cause electrical shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools: Tools with rubber or plastic handles keep you safe from electric shock if something goes wrong.
- Hire a Professional: If you’re unsure about something, it’s always safer to ask a professional electrician for help.
- Follow the Rules: Always follow the electrical codes and safety rules. These rules are made to keep everyone safe.
By following these simple safety tips, you can stay safe and work with electrical wires without worries.
Advantages of Electrical Wire
Electrical wires are important because they carry electricity to power our devices safely. They help make things like lights, phones, and computers work, making our lives easier and more connected.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
Disadvantages of Electrical Wire
Electrical wires are important, but they also have some drawback. They can be dangerous if not installed correctly and may wear out over time, causing problems.
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
FAQs about Electrical Wires
What is an electrical wire?
- An electrical wire is a material that carries electricity from one place to another. It has metal inside (usually copper or aluminum) that helps the electricity flow easily.
What are the different types of electrical wires?
- There are many types of electrical wires. Some common ones are:
- Non-Metallic (NM) Cable: Used in homes to carry electricity safely.
- Underground Feeder (UF) Cable: Used for outdoor or underground power.
- THHN/THWN Wire: Used in buildings for circuits that need high heat resistance.
- Armored Cable (AC): Covered with metal for extra protection.
How do I choose the right wire?
- You need to think about where the wire will be used. Will it be inside or outside? Will it carry a lot of power? It’s also important to make sure the wire is the right size for the job.
Can I use any wire for my electrical work?
- No. It’s important to use the right wire for each job. Some wires are made for inside use, and others are for outside or underground. Using the wrong wire can be dangerous.
What happens if the wire is too small for the job?
- If the wire is too small, it can overheat and catch fire. It’s important to choose the right size so that the electricity can flow safely.
What does “insulated wire” mean?
- Insulated wire means the wire is covered with a protective material (like plastic) to keep the electricity inside and prevent it from shocking you.
Is it safe to touch electrical wires?
- No, it is never safe to touch electrical wires. They can give you a shock, which can hurt or even kill you. Always be careful around electrical wires.
What is the difference between a “live” wire and a “neutral” wire?
A live wire carries electricity to the device (like a lamp), while the neutral wire helps return the electricity back to where it came from.
How can I tell if a wire is safe to use?
If the wire looks damaged or the plastic cover is broken, it’s not safe. You should always check the wire for any visible damage before using it.
Should I hire a professional to install electrical wires?
Yes, if you’re not sure about how to install electrical wires, it’s best to hire a professional, like an electrician. They know how to keep things safe.
Conclusion
Electrical wires are super important because they help bring electricity to our homes, schools, and other places. There are many types of electrical wires, like the Non-Metallic (NM) cable, Underground Feeder (UF) cable, and THHN wire, each made for different jobs.
When choosing the right wire, it’s important to think about where you will use it and how much power it will carry. Always make sure the wire is safe and fits the job.
You May Also Visit It
Cast Iron Melting Temp | Discover Its Industrial Secrets
Metal Stamping Aluminum | Easy Steps to Understand Metal Stamping
Diagram of V8 Engine Explore the Power Behind Every Part
Welding Position | Types, Properties and Uses – Pros and Cons
What is Cold Roll Steel: Types, Grades and Uses | Pros and Cons
Please Write Your Comments